Covid-19 primarily affects the respiratory system while having less of an impact on other organs. It has diverse health manifestations, ranging from asymptomatic to acute respiratory failure. People who develop COVID-19-related respiratory failure may need intensive mechanical ventilation or may pass afterwards.
In this new era, the virus is an issue. The two primary lung disorders in COVID-19 patients are acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and lung failure. Although COVID-19 vaccines are currently accessible, it is vital to identify new therapies to lessen the virus’s effects on people who are already unwell.
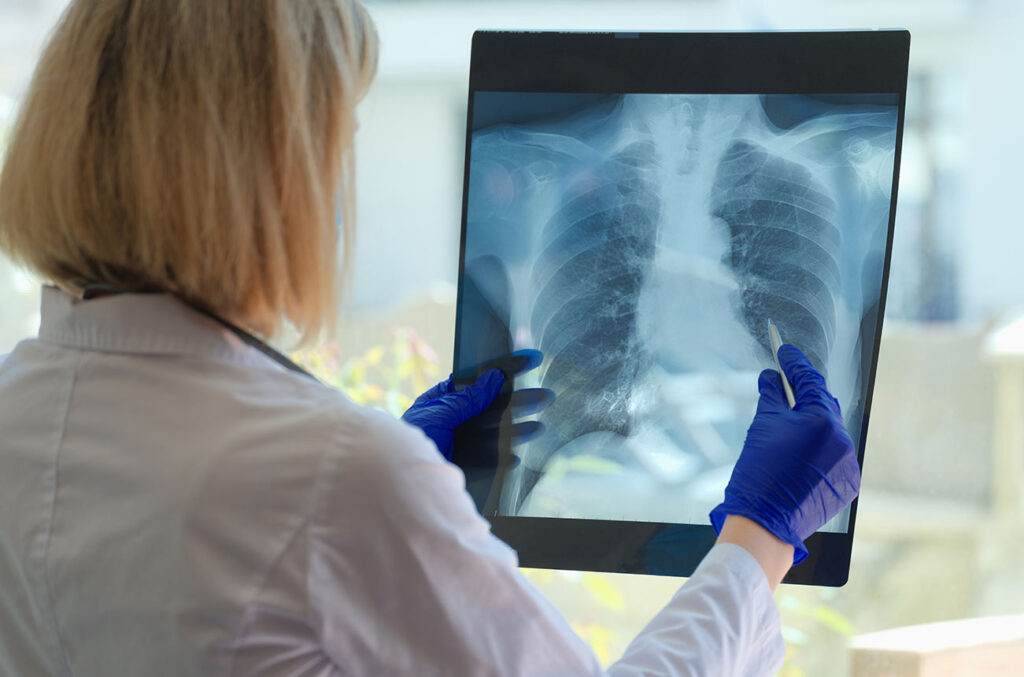
The most common complication of Covid-19 illness is respiratory system dysfunction. Fever, dyspnea, and other severe respiratory signs are manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia, which can result in intractable pulmonary failure. A deadly form of respiratory failure known as acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a prevalent complication for COVID-19 patients.
Fluid accumulation in the alveoli (air tubes in the lungs) leads to acute respiratory distress syndrome. Due to the fluid, the lungs cannot receive adequate air, resulting in less oxygen reaching the circulation. The organs are, however, deprived of the oxygen they require to operate. ARDS usually affects those who are already severely ill or have severe wounds. The primary symptom of ARDS, severe shortness of breath, occurs a few hours to a few days after the injury or infection that causes it.
According to its specificity, the severity of COVID-19 ARDS is classified into three stages: mild, mild-moderate, and moderate-severe. Therefore, COVID-19 ARDS patients require mechanical breathing longer than patients with non-COVID-19 ARDS. Many ARDS sufferers don’t make it out alive. Age and sickness severity both raise the probability of death. Among those who do survive ARDS, some make a full recovery while others have lung damage that lasts a lifetime.
Symptoms of ARDS
The symptoms of ARDS can vary in chronicity, depending on its source, severity, and the presence of preexisting heart or lung disease. They include:
Severe shortness of breath
Laboured and unusually rapid breathing
Low blood pressure
Confusion and extreme tiredness.
What raises the risk of ARDS?
An infection, environmental exposures, personal habits, or some other medical condition may elevate our risk of developing ARDS. Risk factors can differ depending on age, general health, location, and the healthcare facility where we receive care. Doctors will diagnose ARDS and then develop a treatment plan that increases oxygen levels and addresses underlying reasons based on knowledge of the causes and risk factors.
Infection
The most typical risk factors for ARDS are infections. The most prevalent ones are flu and other viruses like respiratory syncytial virus and SARS-CoV-2, which causes COVID-19. Other issues include; Pneumonia, sepsis (a condition in which bacteria infect the bloodstream) and lung damage to a newborn (caused by a uterine infection in a mother).
Environment
We may become more susceptible to ARDS after exposure to air pollution for several weeks or months.
Lifestyle habits
Habits that are unhealthy for the lungs increase the possibility of developing ARDS. They consist of heavy drinking, excessive use of illicit drugs, and smoking.
Can you prevent ARDS?
Taking the following actions can help you reduce the risk of developing ARDS:
Take routine vaccinations to fend off diseases like the flu and COVID-19.
Avoid smoking or staying around smokers.
Be careful how much alcohol you consume.
Reduce your exposure to pollutants as much as you can.
As predators of the respiratory system, ARDS and COVID-19 are closely related, and both lack an effective cure. Therefore, receiving a COVID-19 vaccine is one approach to reducing the risk of developing ARDS if you have any of the risk factors. Vaccination can also stop a COVID-19 infection from becoming more severe. However, if you or someone else with COVID-19 suffers breathing issues, you should seek emergency medical care immediately. You can order a PCR test kit online to be sure you are not suffering from covid-19 infection.Covid-19 is a respiratory-focused infectious disease. The novel Coronavirus infection that causes