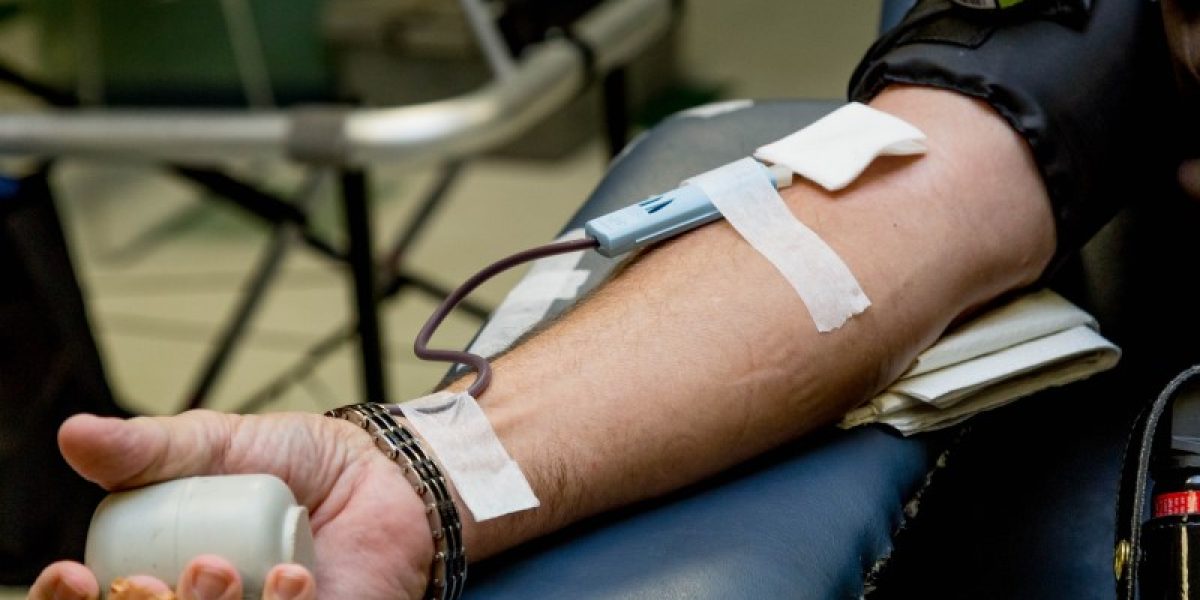
Blood transfusions are an integral part of healthcare in all medical facilities. With the dawn of the pandemic, the adequate and safe availability of blood to meet patient needs became a significant concern. The fear of getting infected with the virus while transfusing blood was a huge problem. Blood transfusion centres in many parts of the country faced difficulties, thus generating a shortage of blood services and blood donors. New policies were implemented, like providing spacious rooms, free blood screening, and keeping the beds at a distance were to this effect.
Transfusions of blood and blood products save lives every year. There is a need for blood and plasma every day to assist covid-19 patients, cancer patients, new mothers and babies, people with immune inadequacies, and people who need surgery. Currently, there’s no evidence anywhere in the world that coronavirus or other respiratory viruses can get transmitted through blood transfusion. Nevertheless, there are some advantages and disadvantages of blood donation. They are:
Advantages of Blood Donation
Only healthy people are eligible to give blood with donors screened upon entry for any indication they may be unwell or infected. Social distancing and hygiene measures are also in place, including screening donors, wearing gloves, and wiping down surfaces after every donation. If you are between 18 and 60 years of age, in good health, weigh at least 50kg for males or 45kg for females, and with good blood pressure, you can be a donor. The advantages of blood donation include:
Helps Covid-19 patients
People who have survived the virus may be able to help others with the infection by donating blood plasma. Their plasma could contain antibodies to the virus. If the infected person receives this blood-containing plasma, it may assist their body fight the virus. We can also get a free private corona test in the process of testing for blood donation.
Identifying adverse health effects
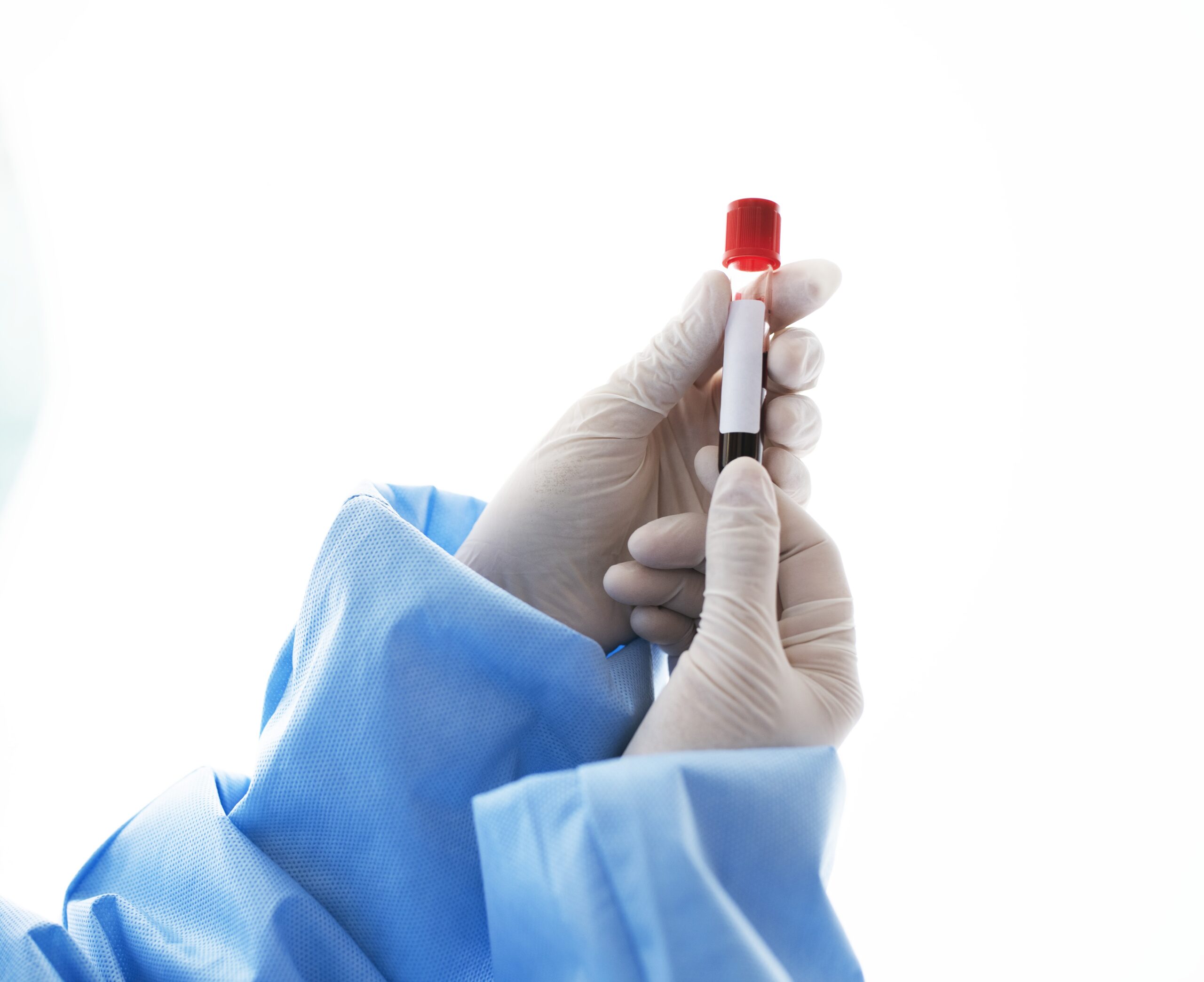
Each person who donates blood during the pandemic completes a simple biological examination and blood test before donating blood. These are not comprehensive tests, but they may help detect unknown health problems, such as anaemia, covid-19, and high or low blood pressure. The test will check the person’s: blood pressure, body temperature, heart rate, and iron levels. If it reveals a problem, the person will not donate blood. These tests include the cheap PCR test London, and those who visit Edgware community hospital can get the Leicester Square blood test. However, the results could be a first step toward seeking treatment.
Reduces iron levels for those with Hemochromatosis
We need iron in the body to produce red blood cells. However, some people have hereditary hemochromatosis. People with this and other kinds of hemochromatosis have excess iron in their blood. The iron can go into different organs, such as the liver and heart, and affect how these organs function. People with this issue are allowed to donate blood. Therefore, for those with hemochromatosis, blood donation can be a treatment option and equally a way of assisting others.
Disadvantages of Blood Donation
Blood donation is safe so long as the centre follows the standard procedures. These include; screening donors for existing health issues, strictly adhering to the covid-19 safety measures, using new needles for each donation, and providing care to ensure a safe recovery. However, there are some possible disadvantages of donating blood. They include:
Temporary reactions
Sometimes, we can experience side effects after donating blood. Although adverse effects are rare, temporary reactions can occur, including weakness, dizziness, feeling faint, lightheadedness, nausea, bleeding from the needle prick, bleeding under the skin, or bruising. These symptoms usually disappear within 24 hours.
Adverse effects
In rare cases, we may experience more serious adverse effects, such as low blood pressure, muscle contractions, breathing difficulty, fainting, vomiting, and convulsions. These effects are more likely to affect younger donors, those with low weight, and individuals donating for the first time.
Before donating blood, we are encouraged to drink enough water, get enough rest, avoid smoking and drinking alcohol, avoid heavy physical activity, and eat enough food rich in iron and protein. Our body replenishes the blood volume within 24 hours, red blood cells within 3 to 5 weeks, and the lost iron in 5 to 8 weeks. We can donate regularly. Men can donate every three months and women every four months.
Donors are always needed to replace those who can not give due to illnesses or other conditions. It takes less than an hour to donate blood, but it can change the lives of many.