The covid-19 infection causes diverse organ diseases, with high dominance of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and digestive tract complications. The virus induces various symptoms, from asymptomatic to multiple organ malfunction, and is categorised from mild, moderate, acute, to crucial depending on the intensity of its manifestation. The most prevalent signs of COVID-19 are fever, cold/cough, nausea, and exhaustion. However, the elderly, immunodeficient people, comorbid patients, and smokers are at an increased risk of vulnerability.
Tobacco is harmful to your health regardless of how you smoke it. Tobacco products do not contain any safe elements, including acetone, tar, nicotine, and carbon monoxide. The substances you inhale have an impact on more than just your lungs. They have the potential to affect your whole body. Its use can cause several health problems in the body and also prolonged effects on your body systems. While smoking increases your risk of various issues over time, some of the physical impacts are immediate.
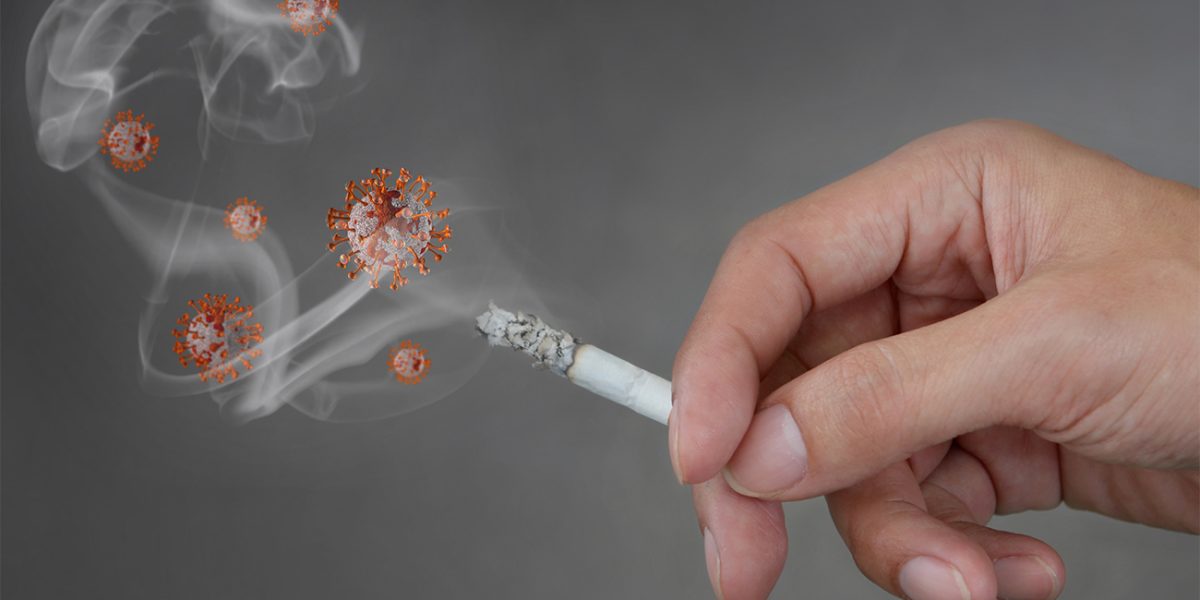
Smoking is a known catalyst for respiratory tract inflammation, allergy, mucus formation, and impaired mucociliary clearance. It increases the risk of many bacterial and viral respiratory illnesses and is equally associated with the worst effects in infected people. It is a well-known risk factor for various respiratory and cardiometabolic diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and bronchial asthma.
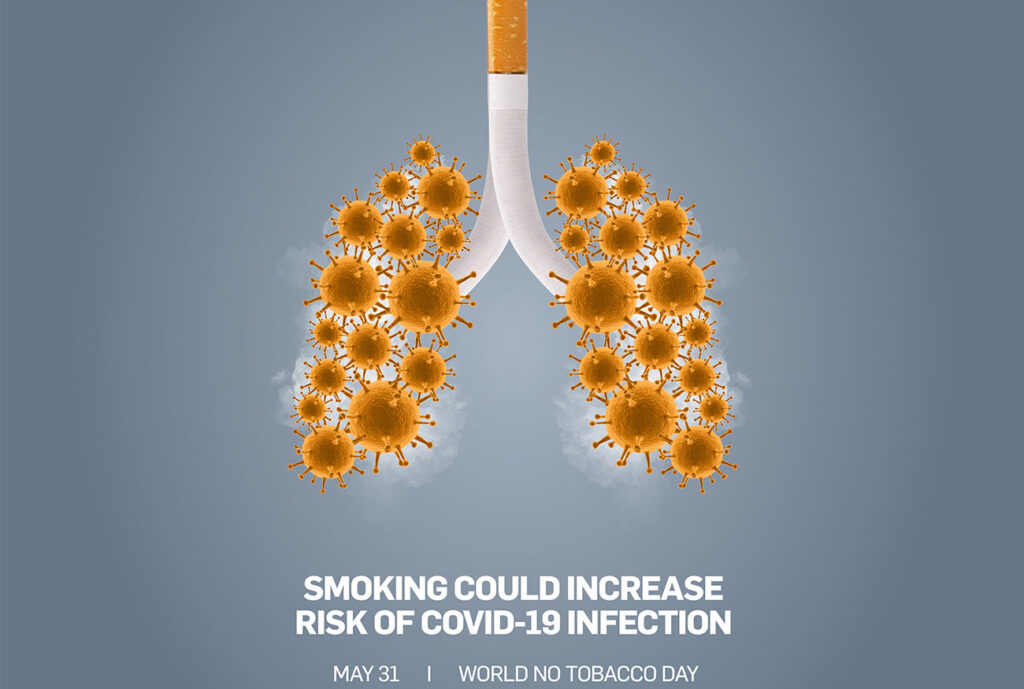
Compared to people who do not smoke, acute or chronic smokers are more likely to develop infections, tuberculosis, pneumonia, and ARDS with extreme complications. They are more liable to various comorbidities as well. Such as emphysema, atherosclerosis, and immune dysregulation. All of which contribute to the emergence and development of COVID-19. Smoking is known to cause vascular endothelial damage, which is a defining feature of COVID-19. It compromises immunity and thereby reduces the efficiency of the organs and antibodies in fighting off diseases and viruses.
Although smoking may not significantly increase the risk of infection, smoking while experiencing covid-19 symptoms may double the risk of its severity. The fundamental mechanisms involving biological and inflammatory signalling pathways stimulated by COVID-19 infection can be drastic for smokers. Smoking reduces lung immune function and damages upper airways, thereby increasing the chances of contracting the virus and the severity of infectious diseases.
For covid-19 infected smokers, the type of symptoms experienced with the smoking level showed that fever is the most frequent symptom, followed by chronic cough, headache, muscle ache, sore throat and severe chest pain. Less frequent symptoms present in patients include chills, shortness of breath, diarrhoea, and abdominal pain. Additionally, some patients with a smoking history had a risk of in-hospital mortality while, others required intensive care and mechanical ventilation.
For other patients, the symptoms experienced (chronic cough, cold, headache, breathing difficulty, and loss of smell) were a possible infection of covid-19 or the damages smoking had done to the body. These damages include heart disease, stroke, lung diseases, diabetes, emphysema and chronic bronchitis. Most of these diseases have similar symptoms to covid-19. And as such a PCR test London is necessary for proper medical examination of the body.
It is therefore evident that discontinuing smoking practices should be considered a part of the strategies to address COVID-19 infection management as smoking increases both the likelihood of symptomatic diseases and the frequency of diseases. Its prevention and cessation should remain a priority for the public, physicians, and public health professionals during a global and national crisis such as the COVID-19 pandemic.
In addition, vaccination is necessary as it aids the immune system to a large extent. Both infected and uninfected persons who are smokers are encouraged to get vaccinated. The vaccines help to boost the immune system which is likely to be impaired due to the unhealthy intake of various substances by smoking. Taking booster shots or any other shot of the covid-19 vaccine puts you in a safer space than going without the vaccine. An adequate diet with proper hydration also improves the immune system.